Author:
Aliya Izet Begovic Yahya and Nofita Sri Wijayanti Kusumawardani
Abstract
ICT in this era has affected all aspects of life and has been widely used in all sectors of human life including education. Integrating ICT into learning is one of the implementations of ICT in the educational aspect. Therefore, one of the important competencies of an educator in improving the ability of sailor school students to support their professional abilities is the Maritime English course. This study designed the integration of ICT in the Maritime English Course syllabus. This study aims to design a Maritime English course syllabus focused on level 2 cadets, based on integrated ICT competencies for the Port Shipping Management (KALK) Program at STIP Jakarta. This study uses Design and Development Research (DDR) as a research design and qualitative research methods. The stages used by DDR in this study are Need Analysis; Design Preliminary Research, Evaluation, Revision, and Design of Syllabus Prototypes. This analysis incorporates ICT competencies proposed by UNESCO, Digital Media Descriptors from the European Profiling Grid (EPG), and other ICT-based theories. The results of this study found that ICT competence is mostly integrated into Learning Outcomes, Teaching Methods, Learning Activities, and Assessments explicitly or implicitly. This study provides ICT integration procedures and designs a syllabus (in prototype form) in the Maritime English course for level 2 cadets in the Port Shipping Management (KALK) Program at STIP Jakarta. The resulting syllabus design is a product-oriented Content Based Syllabus.
Keywords: ICT competencies, syllabus design, ICT UNESCO framework.
Introduction
Technological developments bring various changes and updates to human life. Almost all areas of life cannot be separated from the use of ICT. ICT itself is an extension of Information and Communication Technology, that has definition as technology used to communicate and create, manage and distribute information (UNESCO,2011). Generally, ICT includes computers, internet, telephone, television, radio and other audiovisual equipment (Revita, Tiffany:2022).
ICT has become an integral part of everyday life for many people. This increases its importance in people’s lives and it is expected that this trend will continue, to the extent that ICT literacy will become a functional requirement for people’s work, social, and personal lives. ICT has various benefits, especially technology that can help and make it easier for society and the government to manage and develop maritime economic potential. One of the factors supporting the success of the maritime sector is sea transportation. Sea transportation has long been the most effective means of transportation for large goods and for long journeys. The maritime industry is no longer seen as just another tool for delivery, but has also been seen as one of the important players in development of cities, regions and national economies (Hall and Jacobs, 2012).
Taking advantage of modern ICT developments needs to be realized in the development of prospective seafarers through education and training, especially for Sailing school cadets under the auspices of the Ministry of Transportation. One of the majors that plays a role in advancing the maritime industry is the Port Shipping Management (KALK) major. Port Shipping Management (KALK) is a department that educates and trains graduates to become sea and port transportation management experts who master national and international transportation management systems (PIP Semarang: 2019). According to the Regulation PP Menteri Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia No.22 Th.2016 states that the use of ICT in education adds value to the teaching and learning process, by increasing the effectiveness of learning, or it could be said by adding dimensions of learning that were previously not available. ICT can also be a significant motivational factor in student learning, and can support student involvement in collaborative learning (Purwanto: 2015).
Improving the quality of education is very important because education is a very important need for Indonesia’s future generations in developing maritime potential. The essence of education is to humanize humans, develop the basic potential of students’ intelligence so that they are brave and able to face the problems they face without feeling pressured, able and happy to improve the character of their caliphate on earth (Izzati, Restu Sani in Baharun, Hasan: 2018). In integrating ICT into the teaching and learning activity curriculum and planning it systematically, the curriculum has a very important role in the educational activities being implemented (Kurniasih: 2007). Educational activities carried out formally or informally will not be in accordance with achieving targets if the curriculum is not prepared with a good concept and its implementation is programmed as well as monitoring implementation and evaluation (Hasan: 2018). Education is also often interpreted as a human effort to humanize humans. So that they are able to fulfill their duties as human beings and become individuals who are meaningful citizens of the country and nation. In this case the curriculum has three roles, namely a conservative role, a critical or evaluative role, and a creative role. These three roles in the curriculum are very important and need to be carried out in a balanced manner (Ansyar in Hasan: 2018).
Curriculum Development is the step-by-step process of designing and improving courses offered at schools, colleges, and universities. Although each institution has its own process, the general stages of this framework consist of analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation.
The curriculum development process regularly organizes what will be taught, who will be taught, and how it will be taught. Each component influences and interacts with other components. For example, what is taught is influenced by who is being taught (e.g., developmental stage, age, maturity, and education). The method by which content is taught is influenced by who is taught, their characteristics, and the environment. Curriculum refers to the specific lessons and academic content taught in schools and educational institutions for a particular course or program. On the other hand, curriculum development is a process that aims to perfect the curriculum using various approaches (Gwen: 1996). In developing an effective curriculum and integrated ICT, we hope it will help facilitate educational programs that enrich and improve the quality of students with teacher creations guided by the learning syllabus.
When team individuals talk diverse dialects, there may be perplexity within the meaning of the expressions they are attempting to pass on. Some of the time ships and mariners traveling around the world arrive at neighborhood ports. Ships that dock in some cases have the hail of one nation, have a captain from another nation, and a team from a distinctive nation. Without understanding the same dialect, there will be difficulties in passing on informational to harbor officers and transport group, of course too for harbor officers who have graduated from the Harbor and Shipping Administration (KALK) office. Typically, where Sea English comes into play. Based on the basics of ordinary English, certain sea terms have been received by the sea and shipping community. By having a interesting set of terms for this space, this disposes of the plausibility of perplexity in meaning. The most issue with utilizing typical terms like cleared out or right, front or back, etc. is equivocalness related to heading (Ajay:2021).
In analyzing the joined information, apart from alluding to ICT concurring to UNESCO, this inquiries about moreover employments the European Profiling Lattice (EPG) standard, planning ICT competencies. Competencies within the current syllabus must meet the competency measures for the most competencies of EPG-based instructing. The most instructing competencies are included within the European Profiling Grid (EPG). In this investigate, analysts allude to strategy: information and aptitudes as one of the competencies that’s the protest of syllabus plan. The issue is that descriptors as it were cover many subjects. EPG benchmarks are utilized in proficient behavior and organization (North et al., 2013).
Research Questions
The researcher has a main research question with three sub questions which are mentioned in following part.
Main Question:
How are ICT competences – integrated speaking syllabuses for Maritime English Course?
Sub Questions:
- To what extent are the ICT competences integrated in the existing Maritime English Course syllabuses?
- How are the ICT competences integrated in the Maritime English Course Syllabuses?
- How are the designs of ICT competences – integrated Maritime English Course Syllabuses?
Purpose of Research
In line with the research questions, this study presents the purposes of the research, which are mentioned in the following part.
Main Purpose
To design ICT competences – integrated syllabuses of Maritime English Course.
Sub purposes of this present research are:
- To analyze the ICT competences integrated in the existing Maritime English courses.
- To describe the procedures of designing process of ICT competences – integrated Maritime English Courses.
- To design ICT competences – integrated syllabuses of Maritime English Courses
Theoretical Review
Information and communication technologies ICT
Information and communication technologies (ICT) is the utilize of computing and media transmission innovations, frameworks and apparatuses to encourage the way data is made, collected, prepared, transmitted and put away. It incorporates computing advances like servers, tablet computers and computer program applications, as well as the wired and remote communication advances that back phones, the Web, the Web of Things (IoT) and the metaverse. The objective of ICT is to make strides get to to data and and make human-to-human, human-to-machine and machine-to-machine (M2M) communication simpler and more proficient (Rose:2023). It also characterized as a assorted set of mechanical instruments and assets utilized to transmit, store, make, share or trade data (UIS:2009). These innovative apparatuses and assets incorporate computers, the Web (websites, blogs and emails), live broadcasting innovations (radio, tv and webcasting), recorded broadcasting innovations (podcasting, sound and video players, and capacity gadgets) and communication (settled or portable, partisan, visio/video-conferencing, etc.).
Syllabus and Syllabus components
A syllabus can be characterized as a comprehensive record that traces the substance, structure, and destinations of a course or program of think about. It serves as a contract between the teacher and the learner, building up the desires, duties, and learning results for the instructive travel ahead. Richard (2001) characterizes a syllabus as a determination of the substance of a course of instruction and records what will be instructed and tried. So the instructing and learning prepare must be guided by the syllabus in arrange to form it simple for instructors to carry out learning exercises.
The concept of a syllabus can be followed back to antiquated Greece, where it alluded to a rundown of themes to be secured in a course. Over time, the syllabus has advanced to ended up a more point by point and organized record, enveloping not as it were the course substance but too evaluation strategies, required assets, and arrangements. The essential reason of a syllabus is to supply a guide for successful instructing and learning, guaranteeing clarity, organization, and coherence within the instructive prepare (Team Mrm:2023).
With respect to the syllabus component, Instruction in Indonesia has its claim measures that have been controlled in enactment. Permenristekdikti No 44, 2015 states that there are 8 components in a syllabus counting; a.) Essential data, b.) Learning result, c.) Standard competence, d.) Learning materials, e.) Learning strategies, f.) Time allotment, g.) Appraisal, and h.) References (Bilfaqih, 2015), moreover Agreeing Permendikbud No 49 of 2014 chapter 12 passage 3 expressed that a syllabuses ought to at slightest contain 9 components, they are; (1) Title of the consider program, title and code of the course, semester, credits, and lecturer’s title, (2) Learning Results, (3) Learning goals (4) Learning materials, (5) Learning Strategy, (6) Time assignment (7) Learning involvement (8) evaluation criteria and Pointers, and (9) list of the references.
In deciding syllabus components to be utilized by considering the nature and work of the syllabus as communication, arranging apparatuses for educates, preparing plans for understudies, assistive gadgets or assets, and artifacts for educator assessment. Through this book will center on the Permendikti No 44, 2015 which expressed that there were 8 syllabus components as the premise for the planning. In any case, the talk of this book moreover looks at the components of the syllabus proposed by specialists by looking at a few of the similitude and contrasts that exist, so the taking after are chosen; a). Course Depiction, b). Goals, c). Materials, d). Educating Strategy, e). Appraisal. ies.
Curriculum Development.
Educational programs alludes to the principle-driven activities and forms that direct and cultivate noteworthy learning encounters. Educational modules improvement could be a arranged, astute and ponder course of activities that eventually improve the quality and affect of the learning involvement for understudies. The extreme objective of educational programs is to improve the quality and affect of the instructing and learning involvement (North:2013).
Whether planning a course or a program of considers, there are a number of things that must be considered to make significant learning encounters. Educational programs advancement moves past a content-centred approach to one that considers the relationship between the course/program learning results, appraisal of those results, and the exercises and openings designed to facilitate understudy learning. In planning a course or program, designers have to be consider: Assessment: How will learners and instructors know in the event that the learning results have been finished?, Exercises: What has to be done to realize the learning results? Educational programs Improvement is the step-by-step handle of planning and progressing the course advertised at schools, colleges and colleges. Indeed in spite of the fact that each institution will have its possess prepare, the wide stages of the system comprise of analysis, design, implementation, and assessment. Educational programs alludes to particular lessons and scholastic substance instructed in schools and instructive organizing for a specific course or program (Purwanto:2018). On the other hand, educational programs advancement may be a handle that points to make strides the curriculum by utilizing different approaches. Few of the commonly utilized procedures incorporate require and errand investigation, objective plan, choosing suitable educating and learning strategies, choosing evaluation strategies, and shaping the educational modules committee and educational modules audit committee. Thus the complete prepare is partitioned into fragments to guarantee the improvement of an viable educational modules that would offer assistance to encourage an enhancing instructive program.
The European Profiling Grid
The European Profiling Grid (EPG) , may be a system with descriptors crossing six ‘development phases’ in a dialect teacher’s proficient advancement (European Union, 2011). The EPG is accessible in 13 dialects and is being utilized by schools, colleges and language instructing teach in numerous nations to assist dialect instructors survey their proficient qualities and preparing needs, and to back individuals who are overseeing and supporting instructors. The descriptors within the Profiling Framework cover four key zones: Qualifications, teacher training, and experience Core competences: 1)methodology – knowledge & skills, 2)lesson and course planning, 3) interaction with and monitoring of learners, 4)assessment, 5)‘Enabling skills’, such as language awareness, intercultural competence and the ability to use digital media. 6)Professionalism.
Related Studies
Talking about previous study in this research’s topic. Pritchard, Boris in 2003 from Faculty of Maritime Studies, University of Rijeka, talked about Maritime English syllabus for the modern seafarer. The nature of maritime English, needs analysis, and its connection to the Maritime Education and Training (MET) system are the basis for this article’s discussion of some theoretical and practical aspects of syllabus design. Currently, there are primarily two methods that may be used to analyze the place of Maritime English in the total MET course syllabus:
A simple strategy that is training-focused,
(b) an extensive, or all-inclusive, instructional strategy.
The IMO STCW Convention 1978/1995 for seagoing certificates of competence and, to some extent, the ISM Code’s unavoidable minimum criteria are the only requirements that are covered by the minimal approach to the Maritime English syllabus. The subject within the overall MET curriculum and ensures the future holder of a maritime academic degree efficient competence in English for conducting both sea and shore-based duties. To this end, the growing role and importance of General English within the Maritime English syllabus is emphasized. In order to be able to study the modern developments in Maritime English, a proposal is made for starting an international project of compiling and maintaining a web-based corpus of Maritime English, i.e. a textual and terminological database to be at the disposal of the students, Maritime English teachers and subject teachers in their research, learning and teaching activities.
Another researcher in this scope, Hafita, Ayu Yuniar in 2018. The research was done to create a detailed plan for teaching English to maritime students in their first semester. The plan meets the students’ needs and follows the guidelines of the IMO Model course 3. 17 This research used a descriptive method and involved four alumni, four English lecturers, and twenty-five seventh semester students from Merchant Marine Polytechnic of Makassar. We used questionnaires, interviews, and document review to collect data. We analyzed the data both by counting and measuring (quantitatively) and by describing and interpreting (qualitatively). The survey was used to get information from students about what they need to learn. Next, interviews were conducted with former students to gather additional information about what they need to learn. We interviewed teachers to learn about the current Maritime English lesson plan. The document review was about the IMO Model Course and the current maritime English syllabus. The research found that students in the nautical department need to learn four English skills, especially speaking and listening, as well as vocabulary and grammar related to maritime topics. The specific topics covered in the IMO Model Course 3. 17 are speaking and writing regarding navigation and giving directions. However, the current maritime English syllabus for nautical students does not meet the requirements of the IMO Model Course and does not cover the necessary language skills and elements. The current syllabus is more focused on general English. The words and how they are put together do not make sense in terms of maritime topics. Not having enough learning activities causes Maritime English.
Another researcher, Also, Melor and others (2012) also did research. This study talks about how teachers can use computers and technology to make their work easier, and how students can use them to learn better. Digital comics are a helpful tool for teaching because they use technology and make learning more engaging. They have a lot of benefits, particularly in creating a fun and interesting learning space. Using digital comics to help low-ability English learners improve their writing skills seems to be a very effective method. This research wants to understand what teacher training participants think about using digital comics to help ESL students who struggle with writing. A group of TESL teacher trainees at a university in Malaysia were asked to fill out a survey with questions. The results indicate that future teachers like using technology for teaching writing, and they think that digital comics are helpful for students who struggle with English writing. However, the trainee teachers didn’t like using digital comics in class because it took too much time and wasn’t practical.
Also Fadhilah Hamid, S., & Sulistyaningrum, S. D. (2019). ICT implementation has been widely used in various aspects of our lives, such as education. One way that technology is used in education is by adding it to the lessons or topics that students are studying. Nowadays, speaking is a very important skill to have. So, this study wants to create speaking lesson plans for English Language Education Study Program (ELESP). It will do this by looking at speaking lesson plans from different universities in Indonesia. The study looked at the skills in using information and communication technology (ICT) suggested by UNESCO, the ways of describing digital media in the English Profiling Grid (EPG), and other theories related to ICT. The study used Design and Development Research as the research design and qualitative as the research method. In this study, there are several stages of DDR. First, there is the Need Analysis, where we understand what is needed. Then, we Describe the Objectives and figure out how to accomplish them by Designing and Developing the Syllabus. Next, we Evaluate the initial version of the Syllabus to see if it works well. Finally, we make any necessary adjustments during the Design Revision stage. The study showed that most syllabuses include the use of technology skills in the teaching methods and classroom activities. The most commonly used level of ICT skills in the current syllabuses is called Knowledge Deepening level. However, the use of technology skills was either clearly or indirectly mentioned in the speaking subject syllabuses. This research shows how to use technology in teaching and learning, specifically in speaking classes. It also suggests three different types of speaking classes that can include technology: General Speaking, Professional Speaking, and Academic Speaking. The proposed syllabuses use a skill-based and functional-notional approach.
Method
This research was conducted for 4 months. Based on the purpose of study, the inquire about plan is Research and Development (R&D). Research and Development (R&D) plan was executed since it is in line with the reason of the think about, which pointed at planning ICT-integrated investigate subject syllabuses for Maritime English. Plan and Advancement Investigate (DDR) is included in one of the Plan inquire about models. Agreeing to (Nurwahida, 2017), plan investigate may be a efficient think about of planning, creating, and assessing the instructive intercession (such as programs, techniques, materials learning, item and framework) as a arrangement to understanding complex issues in instructive hone, which moreover points to progress our information of the mediation as well as the plan advancement. The study’s plan was utilized since it advanced the creation of unused information and approval of existing hones.
Data, Data Source and Instrument
The data, data source and instrument of this research are same as the research questions and the steps of DDR. The data are syllabuses components and related theories of ICT integrated English Maritime syllabus, components of Maritime English syllabus integrated into ICT, statement from the FGD activity containing suggestions and feedbacks from the experts. While the data sources are existing Maritime English syllabuses in Indonesia, the result of analysis from the existing syllabuses and related ICT and CEFR documents. Whereas, the instruments of this research are researcher, ICT competence – integrated syllabus indicators and table of analysis, as well as linguistics and syllabus experts.
Data Analysis Procedure
In analyzing the data, the researcher performed a series of actions to analyze the data. There are 4 kinds of analysis conducted in this research. The first analysis is synthesizing the experts’ theories about syllabus design, standardized Maritime English competence and ICT competence in education to be Maritime English and ICT indicators. This analysis is already conducted during the literature review. The second analysis is analyzing the existing syllabuses. The analysis of the existing syllabuses covers: (a) analyzing the syllabus components, (b) analyzing the ICT competence. These analyses are then followed by the third analysis which is related to the process of designing ICT competence – integrated syllabus. This third analysis is conducted by: (i) analyzing the list of ICT indicators of its possibility to be integrated in the syllabus elements and (ii) the integration and transformation from non-integrated to be ICT competence – integrated syllabus elements. The fourth as the last analysis is to put the ICT – competence integrated elements in sequence and template to be the whole applicable ICT competence – integrated Maritime English syllabuses. The designed syllabuses are then judged by the experts and revised by the researcher.
Result and Discussion
The Analysis of Existing Syllabuses
This segment will clarify the ICT competencies coordinates into the existing syllabus component of the Oceanic English. This address is examined to look for reactions to the discourse within the syllabus. In this manner, the examination of this segment is partitioned into four distinguishing proof areas: to begin with, portraying the syllabus and courses within the syllabus; moment, recognizing the existing syllabus components; moment, recognizing Competencies in Investigate Aptitudes and Proficient Organization and third, identifying ICT competencies. This identification is clarified within the taking after areas within the clarification as takes after;
The description of The Existing Syllabus The discoveries talked about in this chapter are based on this study’s sub-questions and driving questions, as expressed in Chapter I of the investigate address. The syllabus was five syllabuses from different colleges watched within the syllabus of their English Sea. Each College has the same distinctive names, English Sea or English 3/4 in this manner: College A Course title is English Maritim, College B course title is English Oceanic, College C course title is English 3 and 4, College D course title English 3 and 4, and college E course title is English. The components found within the syllabus from a few colleges will be talked about in this dialog. Within the identification and examination prepare, a few components showed up within the syllabus.
The components found are at that point compared with the syllabus components proposed by specialists. It was discussed within the writing survey that some specialists such as Davis (2009), Altman and Cashin (1992), Wolf, Czekansku and Dillon (2013), and Permendikti (2016) recommended different components be included within the syllabus. From the specialists, 15 components were taken, which can be utilized as an layout to be included within the syllabus, counting; Essential Data Course, Course Depiction, Learning Result, Learning Objective, Plan, Materials/ Substance, Assignments, Time Assignment, Strategies, Learning Pointers, Evaluation, Learning Exercises, Educators Data, Assets, Approaches. An clarification of the investigation of the syllabus component is connected in Reference section 4, whereas a rundown of the examination comes about is appeared in Table 1. Underneath
The Analysis of ICT Competences
ICT competencies within the existing syllabus from the English Martime courses are found within the plan component’s Learning Outcome, Teaching Method, Assessment, and Learning Media components. Future analysis is about the involvement of ICT competencies in the existing speech syllabus. The researcher identifies ICT competencies in the syllabus elements: Material/Content, Learning Objectives, Teaching Methods and Assessment. After recognizing competencies, analysts at that point compare competencies within the existing syllabus with the perfect circumstance of how ICT can be coordinates, as clarified within the ICT system in UNESCO, which clarifies the stream of how ICT is coordinates. The investigation found that ICT was basically specified within the Learning Objective among the 7 syllabus components chosen in this courses.
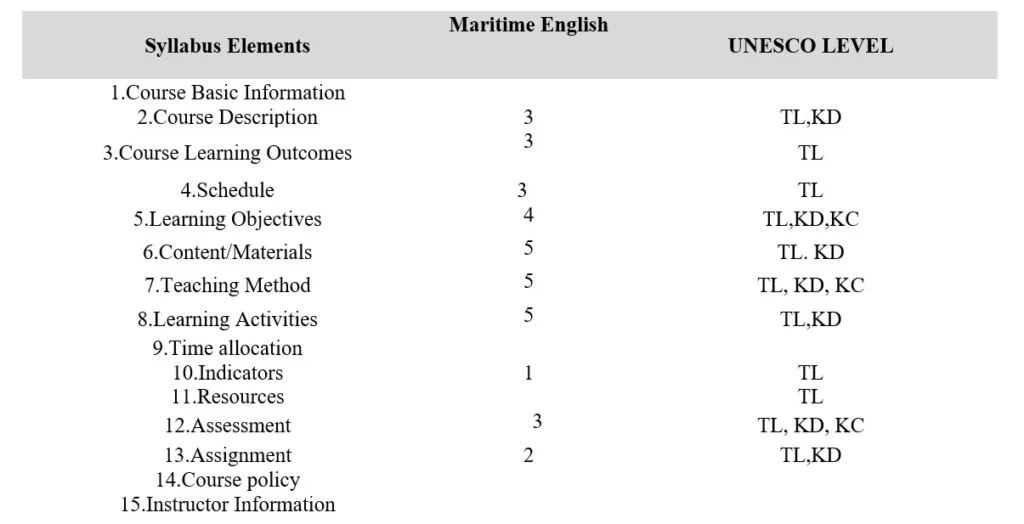
University lecturers who will carry out effective and efficient learning tasks must be distinct from the need to prepare supporters in front of the class. Many things must be done, including making syllabi and semester learning plans (RPS). Designing a syllabus is a systematic writing activity and follows a predetermined procedure; thus, designing a syllabus can be learned as a scientific process in preparing a learning design. The syllabus integrating ICT competencies is a Task-Based Syllabus for Research Skills courses, while for The English and Maritime English courses, courses are Content Based Syllabus. Syllabus components integrated into ICT competencies are basic information, course descriptions, learning outcomes, learning objectives, materials, learning indicators, teaching methods, assignments, assessments, time allocation and learning schedules, policies, and references/resources. In designing ICT competencies integrated into the English and Maritime English courses, several steps must be followed. First, compile the syllabus by the guidance book to compile syllabus in determining appropriate steps by standards (Dikti, 2016); using EPG helps students progress through the level. The EPG is beneficial because it applies the same levels to all career sub-skills and competence areas. Understanding The English and Maritime English courses is included in the professionalism aspect. It looks at the EPG level in the Methodology: Knowledge and Skills and Professionalism aspect at the EPG level 1.1-2.2. This analysis uses the EPG level scale to see ICT competencies integrated into The English and Maritime English Courses syllabus. In integrating ICT competencies, the author also considers Tomei’s book in chapter 10 on Technology Integration(Nafiati, 2021). Lecturers are professional educators and scientists with the main task of transforming, developing, and disseminating science, technology, and art through Education, research, and community service. Core steps such as Planning, Implementing, Controlling, Assessing and Evaluating are needed in compiling the syllabus.

Conclusion
The use of EPG (European et al.) in designing new Syllabuses in the aspects of professional conduct and administration and adding in the aspect of methodology: Skill and Knowledge have become guidelines for language teaching and have been used as reference points to help improve the quality and effectiveness of language training by providing instruments which will improve competence and help the provision and mobility of language teachers. This is used to encourage learning in language education programs to improve competence in ICT, streamline evaluations and have ongoing qualifications. This framework is standardized to formulate objectives, teaching materials and assessments for courses that include The English as ESP and Maritime English courses in Syllabuses design. So the procedure that is passed in this stage is through the stages of research Need Analysis, Stating Objectives, Developing Preliminary Syllabuses, Evaluation, and Syllabuses Prototype.
References
- Altman, H. B., & Cashin, W. W. E. (1992). Writing a syllabus. Research in Higher Education, (27), 1–6. Retrieved from http://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=+Syllabus+shares+%22What+the+Teacher+Wants.%22&hl=en&lr=&btnG=Search#1
- Aydin, Şihmantepe. Improving Maritime English Oral Communication Skills in an Online Environment: Engaging Students as Teams (Piri Reis University, Turkey), Murat Selçuk Solmaz (Piri Reis University, Turkey), and Cihat Aşan (Piri Reis University, Turkey) Source Title: Trends and Developments for the Future of Language Education in Higher Education Copyright: © 2021 |Pages: 21
- Bilfaqih, Y. (2015). Panduan Menyusun Rencana Pembelajaran Semester (Rps).
- BPSDM-KEMENHUBhttps://bpsdm.dephub.go.id/14 September 2023.
- Davies, B. G. (2007). Tools for Teaching. Retrieved from http://weekly.cnbnews.com/news/article.html?no=124000
- Devi, P. K., Sofiraeni, R., & Khairuddin, K. (2009). Pengembangan perangkat pembelajaran untuk guru SMP. 69. Retrieved from https://mgmpmatsatapmalang.files.wordpress.com/2012/07/pengembanganperangkatsmp.pdf
- Dikti, T. (2016). Panduan Penyusunan Kurikulum Perguruan Tinggi.
- Dikti, T. (2016). Panduan Penyusunan Kurikulum Perguruan Tinggi. Retrieved from http://weekly.cnbnews.com/news/article.html?no=124000
- El Sawi, Gwen, Ph.D.Under the guidance and sponsorship ofExtension, Education and Communication Service (SDRE)Research, Extension and Training DivisionFOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS
- ESOL Examinations. (2011). Using the CEFR: Principles of good practice. University of Cambridge, 7(October), 2017.
- Fadhilah Hamid, S., & Sulistyaningrum, S. D. (2019). DESIGNING ICT COMPETENCES – INTEGRATED SYLLABUSES OF SPEAKING COURSES (DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT STUDY OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION PROGRAM SYLLABUSES). IJLECR (International Journal of Language Education and Cultural Review), 5(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.21009/IJLECR.051.01.
- Graves, K. (2000). Designing Language Courses.
- Hackett, S. (2013). the Eaquals Framework for Language.
- Hall, P. V. & Jacobs, W. (2012). Why are maritime ports (still) urban, and why should policymakers care? Maritime Policy and Management, 39 (2), 189-206 Ilmiah Mata Kuliah Umum, 21(2), 151–172. Information and Communication Technology ( Ict ). I(3), 73–85.
- Hafita, Yuniar Ayu:2018. Developing Syllabus for Maritime English of Nautical Department at Merchant Marine Polytechnic of Makassar.
- Ishaq. (2015). Desain Pengembangan Pembelajaran Design Development Based Learning
- Izzati, Restu Sani Izzati, “Implementasi Kurikulum 2013 Bagi Peserta Didik Berkebutuhan
- Kencana Prenada Media Group, 2015). 12
- Khusus Disekolah Dasar Inklusif,” Jurnal Pendidikan Khusus, 2015, 1–8. 2 Kurniasih, “Landasan Filosofis Pendidikan Dan Landasan Pendidikan” (Bandung: UPI, 2007). 13 3 A. Azra, Esei-Esei intelektual Muslim Pendidikan Islam (Jakarta: Logos Wacana, 1998).
- M. Ansyar, “Kurikulum, Hakikat, Fondasi Desain Dan Pengembangan,” (Jakarta:
- Nafiati, D. A. (2021). Revisi taksonomi Bloom: Kognitif, afektif, dan psikomotorik. Humanika, Kajian
- North, Brian, Malteva, Galya & Rossner, R. (2013). The European Profiling Grid. 1–35.
- Nurwahida. (2017). Developing English Materials for STAKPN Tarutung. Thesis, 16(November), 15–265
- PIP Semarang”Program studi DIV KALK.”https://pip-semarang.ac.id/index.php/program-studi-d-iv-talkv2/>14 September 2023.
- Purwanto. Pengembang TeknologiPembelajaran, Kebutuhan, Peluang, dan Tantangandi Indonesia, Jurnal Teknodik Vol. 19 No. 2, Agustus 2015 https://jurnalteknodik.kemdikbud.go.id/index.php/jurnalteknodik/article/view/157/156 Cendekia Vol. 16 No 1, Januari – Juni 2018 41
- Pritchard, Boris:2023Maritime English syllabus for the modern seafarer: comprehensive or safety-related courses?.
- Rome, :1996. Shipsapp- Surya Dharma “Able Engine-Able Deck”, deskripsi website, Informasi, < Artikel/rating-able-engine and deck.html, > [14 September 2023].
- STIP Jakarta”Ketatalaksanaan Angkutan Laut dan Kepelabuhan”, https://stipjakarta.ac.id/ketatalaksanaan-angkutan-laut-dan-kepelabuhan/. (14 September 2023)
- UIS. 2009. Guide to measuring information and communication technologies (ICT) in education. Montreal: UIS.
- UNESCO. (2007). UNESCO ICT Competency Standards for Teachers (pp. 1–16). pp. 1–16. Retrieved from doi: 10.17485/ijst/2009/v2i3/29416
- UNESCO. (2011). ICT Competency Framework For Teacher. Unesco, ث ققثق(ثق ثقثقثق), ثقثقثقثق.
- Wachyu. (2013). Syllabus Design for Teaching English
- Technopedia.”information and Communication Technology.” https://www.techopedia.com/definition/24152/information-and-communications-technology-ict (14 September 2023)
- Marine Insight.”What is maritime English and Why is it important?.” https://www.marineinsight.com/life-at-sea/what-is-maritime-english-and-why-it-is-important/ 14 September 2023.
- Daily Social.”ICT ADALAH.”https://dailysocial.id/post/ict-adalah (14 September 2023)
- Team MRM (June 4, 2023). “What is Syllabus? Definition, Components, Importance of Syllabus and Its Design, Implementation, Challenges and Strategies.” in Domain of Mizanur R Mizan. https://www.mizanurrmizan.info/what-is-syllabus-definition-components-importance-of-syllabus-and-its-design-implementation-challenges-and-strategies/.
- https://camosun.ca/about/centre-excellence-teaching-and-learning/curriculum-development.



